Scipy stats doesnt have Normal Inverse Gamma distirbution.
We would like to incorporate Normal Inverse Gamma distirbution in “scipy.stats” package.
Learning about Normal Inverse Gamma(NIG) distribution will lead you to a plot like this from wikipedia.
It was intruiging enough to find out how to plot this graph in python and was sure that there will be some already plots available. But to my suprise there is no blogs or docs to plot NIG in python. The closest I found was in R langugage in [1] by Frank Portman.
So I spent some time to plot NIG in python below is the snippet for it. Special thanks to Jake Vadendeplas[2] for his wonderful blogs about visualization in python.
Normal Inverse Gamma Distribution
Let the input \(x\) on which its modelled be : \[ x = [\mu, \sigma^2] \]
Probability density function (PDF)
\[ f(x | \delta, \alpha, \beta, \lambda ) = \sqrt{\left(\frac{\lambda}{2 \pi x[\sigma^2]} \right)} \frac{\beta^\alpha}{\Gamma(\alpha)} \left(\frac{1}{x[\sigma^2]} \right)^{(\alpha + 1)} \exp{ \left( - \frac{2\beta + \lambda \left(x[\mu] - \delta \right)^2 }{ 2 x[\sigma]^2} \right)} \]
from scipy.stats import rv_continuousfrom scipy.stats import normfrom scipy.stats import gengammafrom scipy.special import gammafrom scipy.stats import exponimport numpy as np% matplotlib inlineimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt'seaborn-white' )class norminvgamma():r"""A normal inverse gamma random variable. The mu (``mu``) keyword specifies the parmaeter mu. %(before_notes)s Notes ----- The probability density function for `norminvgamma` is: .. math:: x = [ \ mu, \ sigma^2] f(x | \ delta, \a lpha, \b eta, \ lamda) = \ sqrt( \f rac{ \ lamda}{2 \ pi x[ \ sigma^2}]) \f rac{ \b eta^ \a lpha}{ \ gamma( \a lpha)} \f rac{1}{x[ \ sigma^2]}^( \a lpha + 1) \ exp(- \f rac{2 \b eta + \ lamda(x[ \ mu] - delta)^2}{2 x[ \ sigma^2] }) for a real number :math:`x` and for positive number :math: ` \ sigma^2` > 0 %(after_notes)s %(example)s """ def __init__ (self , delta, alpha, beta, lamda):self .argcheck(delta, alpha, beta, lamda)self .delta = deltaself .alpha = alphaself .beta = betaself .lamda = lamdadef argcheck(self , delta, alpha, beta, lamda):return (alpha > 0 ) def rvs(self , size= 1 ):= gengamma.rvs(self .alpha, self .beta, size= size)= np.array(sigma_2)return [[norm.rvs(self .delta, s/ self .lamda), s] for s in sigma_2]def pdf(self , xmu, xsigma2):= ((self .lamda)** 0.5 ) * ((self .beta)** self .alpha)= (xsigma2 * (2 * 3.15 )** 0.5 ) * gamma(self .alpha)= (1 / xsigma2** 2 )** (self .alpha + 1 )= expon.pdf((2 * self .beta + self .lamda* (self .delta- xmu)** 2 )/ (2 * xsigma2** 2 ))#print (t1, t2, t3, t4) return (t1/ t2)* t3* t4def stats(self ):#ToDo return def plot(self ,zoom= 0.9 , axs= None ):= 50 = gengamma.ppf(zoom, self .alpha, self .beta) * self .lamda#print(max_sig_sq) = np.linspace(self .delta - 1 * max_sig_sq, self .delta + 1 * max_sig_sq, num= steps)#print (mu_range[0], mu_range[-1]) = np.linspace(0.01 , max_sig_sq, num= steps)= np.meshgrid(mu_range, sigma_range)= self .pdf(mu_grid, sigma_grid)if axs:= axs.contour(mu_grid, sigma_grid, pdf_mesh, 20 , cmap= 'RdGy' ); = True , fontsize= 8 )#extent=[mu_range[0], mu_range[-1], sigma_range[0], sigma_range[-1]] = [mu_range[0 ], mu_range[- 1 ], sigma_range[0 ], sigma_range[- 1 ]],= 'lower' , cmap= 'Blues' , alpha= 0.5 )'equal' )"(" + str (self .delta)+ "," + str (self .alpha)+ "," + str (self .beta)+ "," + str (self .lamda)+ ")" )#plt.colorbar(); else :assert True , "Pass the axes to plot from matplotlib"
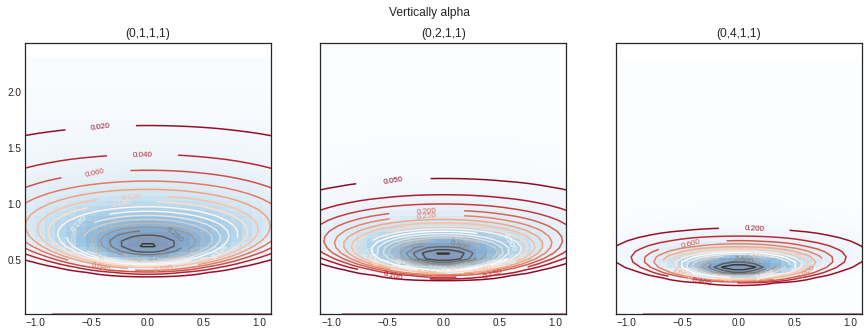
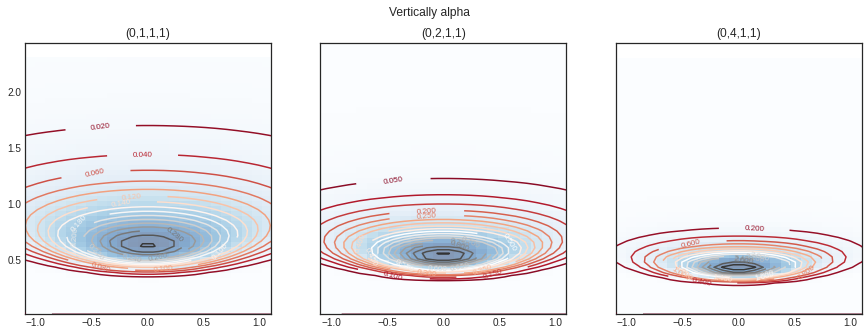
Varying different range of \(\alpha\)
#norminvgamma = norminvgamma_gen() = plt.subplots(1 , 3 , sharey= True , figsize= (15 ,5 ))'Vertically alpha' )= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 1 )= nig.rvs(size= 10 )= axs[0 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 2 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 1 )= 0.7 , axs= axs[1 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 4 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 1 )= 0.2 , axs= axs[2 ])
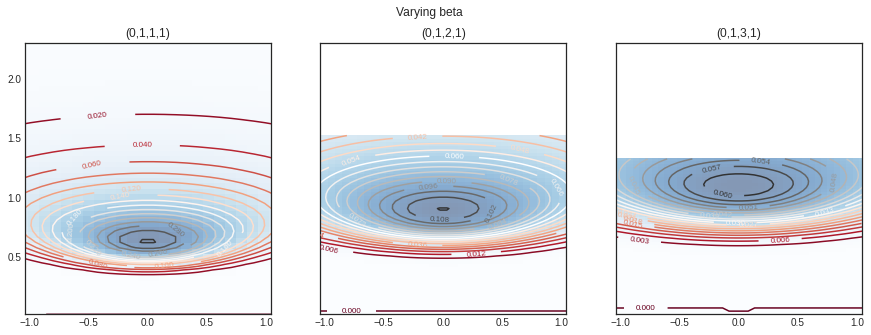
Varying different range of \(\beta\)
= plt.subplots(1 , 3 , sharey= True , figsize= (15 ,5 ))'Varying beta' )= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 1 )= nig.rvs(size= 10 )= axs[0 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 2 , lamda= 1 )= axs[1 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 3 , lamda= 1 )= axs[2 ])
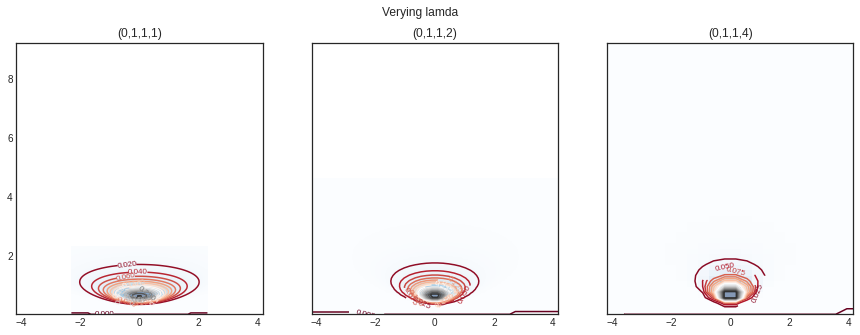
Varying different range of \(\lambda\)
= plt.subplots(1 , 3 , sharey= True , figsize= (15 ,5 ))'Verying lamda ' )= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 1 )= nig.rvs(size= 10 )= axs[0 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 2 )= axs[1 ])= norminvgamma(delta= 0 ,alpha= 1 ,beta= 1 , lamda= 4 )= axs[2 ])
References
https://frankportman.github.io/bayesAB/reference/plotNormalInvGamma.html
https://jakevdp.github.io/PythonDataScienceHandbook/04.04-density-and-contour-plots.html